Numbness in the face is a symptom that can feel alarming, especially when it appears suddenly or affects only one side. It may present as a tingling sensation, reduced sensitivity, pins-and-needles feeling, or complete loss of sensation in areas such as the cheeks, lips, jaw, chin, or around the eyes. While facial numbness is sometimes temporary and harmless, in other cases it can signal an underlying nerve, dental, or medical condition that requires prompt attention.
Many patients ignore early facial numbness, assuming it is due to fatigue, stress, or sleeping in an awkward position. However, persistent or recurring numbness should never be overlooked, as it may indicate nerve compression, infection, dental problems, or systemic medical issues. Understanding the possible causes helps determine when simple monitoring is enough and when professional evaluation is necessary.
This blog explains the common causes of facial numbness, how to recognize related warning signs, and when you should seek medical help.
Understanding Facial Numbness
Facial numbness occurs when the nerves responsible for sensation are irritated, compressed, inflamed, or damaged. The face has a complex nerve network, and even minor disturbances can lead to altered sensation. Numbness may develop gradually or suddenly and can last from a few minutes to several days, depending on the cause.
The most commonly involved nerve is the trigeminal nerve, which supplies sensation to most parts of the face. However, dental nerves, facial nerves, and even nerves from the neck can contribute to facial numbness.
Nerve-Related Causes of Facial Numbness
Trigeminal Nerve Irritation or Compression
The trigeminal nerve is the primary sensory nerve of the face. Irritation or compression of this nerve can cause numbness, tingling, or altered sensation in the cheeks, jaw, lips, or forehead. Causes may include inflammation, trauma, or pressure from nearby structures.
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Although trigeminal neuralgia is more commonly associated with sharp facial pain, some patients experience numbness or tingling between painful episodes. These sensory changes usually affect one side of the face.
Facial Nerve Disorders
The facial nerve controls facial movement but also contributes to sensation. Inflammatory conditions affecting this nerve can lead to facial weakness, drooping, or numbness, often on one side.
Nerve Injury or Trauma
Facial injuries, surgical procedures, or accidental trauma can damage sensory nerves, resulting in temporary or permanent numbness. The affected area depends on which nerve is involved.
Dental Causes of Facial Numbness
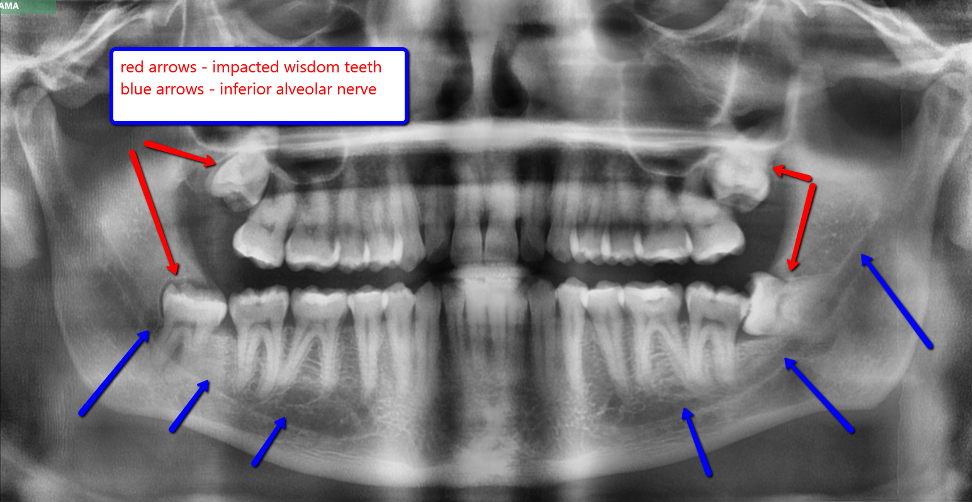
Impacted Wisdom Teeth
Impacted wisdom teeth can press against nearby nerves, particularly in the lower jaw, leading to numbness or tingling in the chin, lower lip, or jaw area.
Dental Infections or Abscesses
Severe tooth infections can spread to surrounding tissues and irritate nearby nerves. This may result in facial numbness along with pain, swelling, and fever.
Dental Procedures
Temporary numbness may occur after dental treatments due to local anesthesia. In rare cases, nerve irritation during procedures can cause prolonged sensory changes.
Jaw Cysts or Lesions
Cysts or growths in the jawbone may compress nerves over time, causing gradual onset facial numbness without obvious pain.
Medical Causes of Facial Numbness
Sinus Infections
Severe sinus infections, particularly in the maxillary sinuses, can cause facial pressure and numbness in the cheeks or upper jaw due to nerve irritation.
Migraine and Headache Disorders
Some migraines are associated with sensory symptoms, including facial numbness or tingling, usually on one side of the face.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Deficiencies in certain vitamins, especially vitamin B12, can affect nerve health and lead to numbness or tingling sensations in the face and other parts of the body.
Neurological Conditions
Certain neurological disorders may cause facial numbness as an early or associated symptom. This numbness may be intermittent or progressive and is often accompanied by other neurological signs.
Circulatory Issues
Reduced blood flow to facial nerves, sometimes related to vascular conditions, can result in temporary numbness or tingling.
Facial Numbness on One Side vs Both Sides
| Pattern of Numbness | Possible Causes | Level of Concern |
|---|---|---|
| One-sided facial numbness | Nerve compression, dental issues, migraines | Moderate to high |
| Both sides of the face | Vitamin deficiency, systemic conditions | Moderate |
| Sudden numbness with weakness | Neurological causes | High |
| Temporary numbness after procedure | Local anesthesia | Low |
Associated Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
Facial numbness accompanied by certain symptoms may indicate a more serious condition. These include facial weakness, drooping, difficulty speaking, severe headache, vision problems, or loss of balance. Such symptoms require immediate medical evaluation.
How Facial Numbness Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis begins with a detailed medical and dental history, followed by a physical examination. Imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI may be recommended to assess nerve pathways, jaw structures, and surrounding tissues. Blood tests may also be used to identify nutritional deficiencies or systemic conditions.
When to Seek Medical Help for Facial Numbness
You should seek professional medical advice if facial numbness persists for more than a few days, worsens over time, or is associated with pain, swelling, or muscle weakness. Sudden onset numbness, especially when combined with difficulty speaking or facial drooping, should be treated as a medical emergency.
Patients experiencing recurring facial numbness should not rely on self-diagnosis, as early intervention often leads to better outcomes.
Treatment Options Based on the Cause
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of facial numbness. Dental-related issues may require infection control or surgical intervention, nerve-related conditions are managed with medications or specialist care, and medical causes may need systemic treatment or lifestyle adjustments. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective and lasting relief.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is facial numbness always serious?
Not always, but persistent or recurring numbness should be evaluated to rule out underlying conditions.
Can dental problems cause facial numbness?
Yes, impacted teeth, infections, or jaw lesions can compress nerves and cause numbness.
Can stress cause facial numbness?
Stress may contribute indirectly by causing muscle tension or nerve irritation, but it should not be assumed as the sole cause.
How long does facial numbness last?
Duration depends on the cause and can range from minutes to several days or longer.
Should I worry about numbness on one side of my face?
One-sided facial numbness should be evaluated, especially if it is sudden or associated with other symptoms.
Can facial numbness be treated?
Most cases can be treated successfully once the underlying cause is identified.
Conclusion
Facial numbness can result from nerve irritation, dental problems, or underlying medical conditions. While some causes are temporary and harmless, others require prompt diagnosis and treatment. Paying attention to associated symptoms and seeking timely medical advice can help prevent complications and ensure proper care. If facial numbness is persistent or unexplained, professional evaluation is always the safest approach.












